
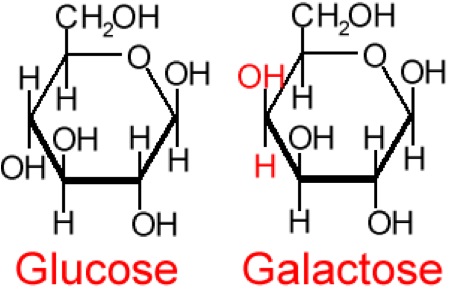
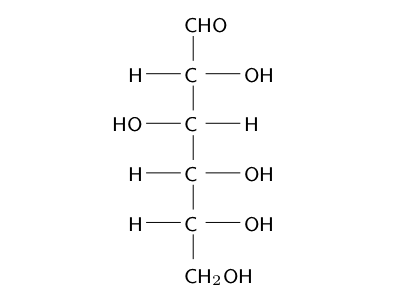
As glucose is a stable molecule, it is impossible for any two OH groups to bind to the same carbon.

The principal energy-reserve carbohydrate in plants, starch, is made of thousands of linear glucose units. It powers cell function, and its metabolism must be carefully regulated.
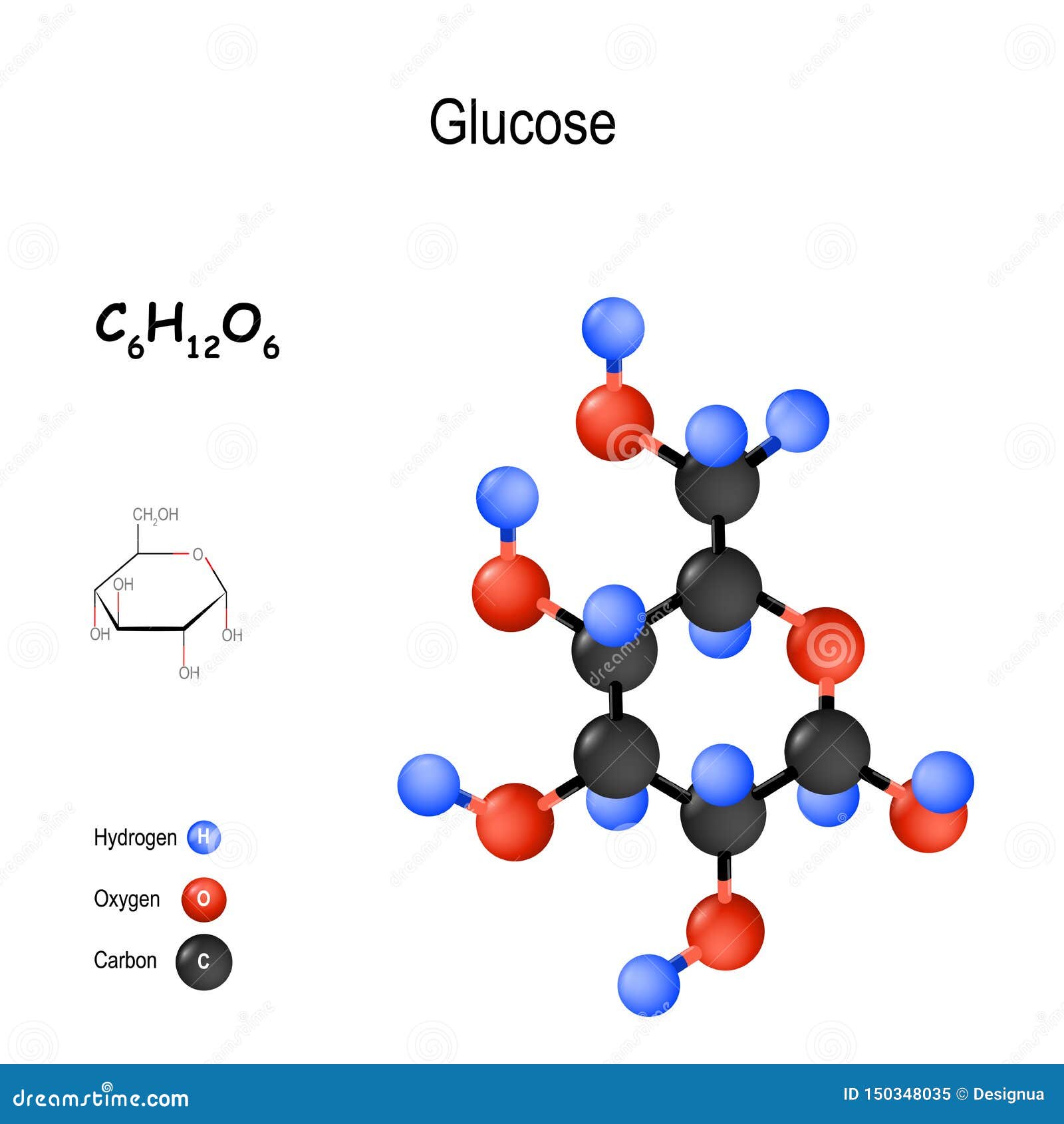
Found in fruits and honey, it is the most common free sugar in higher animals’ blood. It is commonly known as dextrose and belongs to the group of carbohydrates known as simple sugars (monosaccharides). Available fields are: Gene name ( HGNC name or synonyms), Protein class, Chromosome, External identifier ( Ensembl gene, transcript or protein identifier, UniProt accession number, NCBI Entrez gene identifier), Subcellular location based on immunofluorescent staining in three different cell lines, Organ-, Tissue-, Cancer- and Cell line expression, Antibody validation results in four different assays ( IH=immunohistochemistry, IF=immunoflourescence, WB=Western blot, PA=Protein array), evidence scores and a filtration on Genes with antibodies only and Genes with knowledge-based annotated protein expression ( IH, IF).Glucose gets its name from the Greek word glykys, which means sweet.
Specific fields can be searched by using the "Fields"-function. The free text query word needs to be at least three characters long. The free text search will scan for complete and partial matches to gene names, gene synonyms, gene descriptions, external ( UniProt, Ensembl, NCBI Entrez Gene) gene and protein identifiers, protein classes, Gene Ontology identifiers and descriptions, antibody identifiers and image annotations. The search function can be used for free text search (type anything in the search field), or for more complex queries using "Fields" (see examples).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
